Project Kickoff
How the Web works
HTML Basics: Elements, Tags, and Document Structure
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language and is the basic structural element that is used to create webpages. HTML is a markup language, which means that it is used to “mark up” the content within a document, in this case a webpage, with structural and semantic information that tells a browser how to display a page. Doctype. The first line of code, <! … HTML Root Element. Next, the <html element wraps around all of the other code and content in our document. … Head Element. … Body Element.
When client and server software implements WMS, any client can access maps from any server. Any client can combine maps (overlay them like clear acetate sheets) from one or more servers. Any client can query information from a map provided by any server. While programmers need to write code to implement the specifications, end users can take advantage of products that include them to publish and access geospatial information. Software buyers can choose the best solution for their needs and not worry about if it will work with other solutions; if they all implement the same standard (WMS) they will all work together.
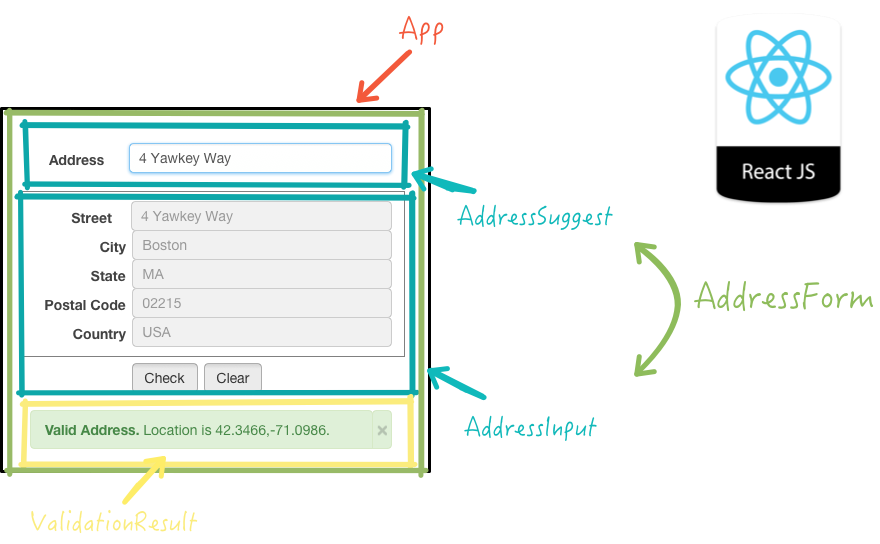
State and Props work
React lets you define components as classes or functions. The methods that you are able to use on these are called lifecycle events. These methods can be called during the lifecycle of a component, and they allow you to update the UI and application states. Props are used to pass data, whereas state is for managing data. … State data can be modified by its own component, but is private (cannot be accessed from outside) Props can only be passed from parent component to child (unidirectional flow) Modifying state should happen with the setState ( ) method

- Mounting
When an instance of a component is being created and inserted into the DOM it occurs during the mounting phase.
- Updating
Anytime a component is updated or state changes then it is rerendered. These lifecycle events happen during updating in this order.
- Unmounting
The final phase of the lifecycle if called when a component is being removed from the DOM
- Mounting
When an instance of a component is being created and inserted into the DOM it occurs during the mounting phase.
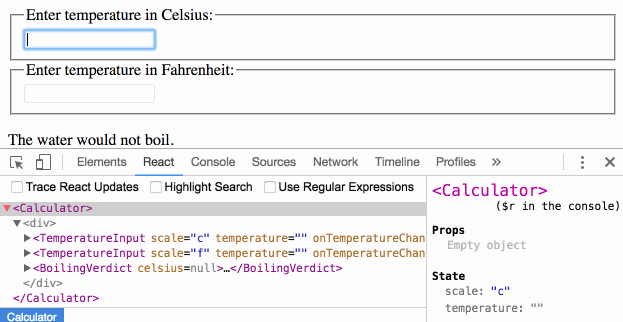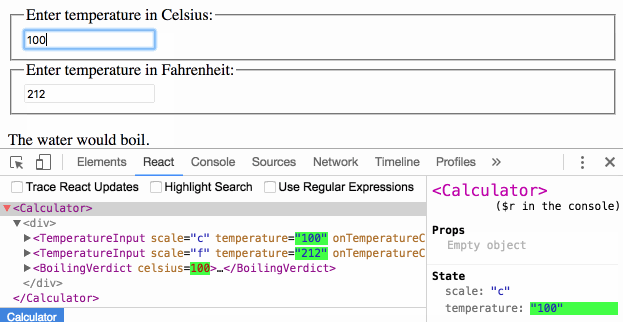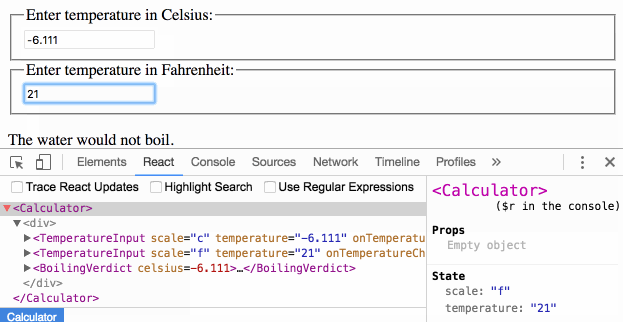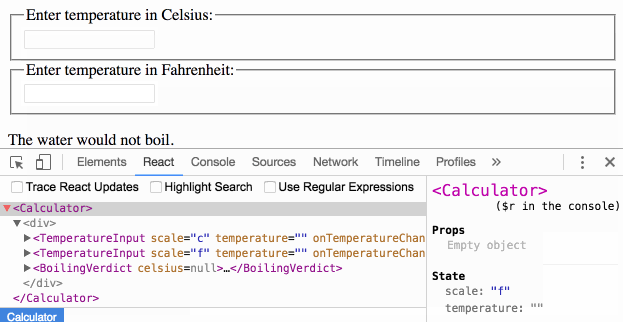
Passing Functions as Props
map()
The map() method creates a new array populated with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
The map() method in JavaScript creates an array by calling a specific function on each element present in the parent array. It is a non-mutating method. Generally map() method is used to iterate over an array and calling function on every element of array.

display each value in JSX
.map() in JavaScript iterates through an array and calls a specified function for each of the items. Components in JSX are JS functions. For each object in the array, a block of JSX elements is returned.
Also, data from the object is passed to each block using the JSX handlebars-like curly brackets.
In the App() component of src/index.js iterate over the imported data using .map()
React and Forms
React Docs - Forms
HTML form elements work a bit differently from other DOM elements in React, because form elements naturally keep some internal state.
Controlled Components
We can combine the two by making the React state be the “single source of truth”. Then the React component that renders a form also controls what happens in that form on subsequent user input. An input form element whose value is controlled by React in this way is called a “controlled component”.
The textarea Tag
In HTML, a (textarea) element defines its text by its children.
The select Tag
In HTML, (select) creates a drop-down list. For example, this HTML creates a drop-down list of flavors
Alternatives to Controlled Components
It can sometimes be tedious to use controlled components, because you need to write an event handler for every way your data can change and pipe all of the input state through a React component. This can become particularly annoying when you are converting a preexisting codebase to React, or integrating a React application with a non-React library. In these situations, you might want to check out uncontrolled components, an alternative technique for implementing input forms.
NODE.JS
What Is Node.js?
Node.js® is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine.

Node Is Built on Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript Engine
The V8 engine is the open-source JavaScript engine that runs in Google Chrome and other Chromium-based web browsers, including Brave, Opera, and Vivaldi. It was designed with performance in mind and is responsible for compiling JavaScript directly to native machine code that your computer can execute.
How Do I Install Node.js?
In this next section, we’ll install Node and write a couple of simple programs. We’ll also look at npm, a package manager that comes bundled with Node.
Node Binaries vs Version Manager
Many websites will recommend that you head to the official Node download page and grab the Node binaries for your system. While that works, I would suggest that you use a version manager instead. This is a program that allows you to install multiple versions of Node and switch between them at will. There are various advantages to using a version manager. For example, it negates potential permission issues when using Node with npm and lets you set a Node version on a per-project basis.
SQL vs NoSQL Database Differences Explained
| SQL | NoSQL |
|---|---|
| databases are primarily called as Relational Databases (RDBMS | NoSQL database are primarily called as non-relational or distributed database. |
| databases uses SQL ( structured query language ) for defining and manipulating the data, which is very powerful. | queries are focused on collection of documents. Sometimes it is also called as UnQL (Unstructured Query Language). The syntax of using UnQL varies from database to database. |
| relational | non-relational |
| vertically scalable | horizontally scalable |
| have predefined schema whereas | have dynamic schema for unstructured data. |
Hybrid Flow
Applications that are able to securely store Client Secrets may benefit from the use of the Hybrid Flow, which combines features of the Authorization Code Flow and Implicit Flow with Form Post to allow your application to have immediate access to an ID token while still providing for secure and safe retrieval of access and refresh tokens. This can be useful in situations where your application needs to immediately access information about the user, but must perform some processing before gaining access to protected resources for an extended period of time. The Hybrid Flow is an OpenID Connect flow which incorporates characteristics of both the Implicit flow and the Authorization Code flow. It enables clients to obtain some tokens straight from the Authorization Endpoint, while still having the possibility to get others from the Token Endpoint.

Things I want to know more about
solveing this error.
for more info please visit my github
## qusaiqeisi
best regard
