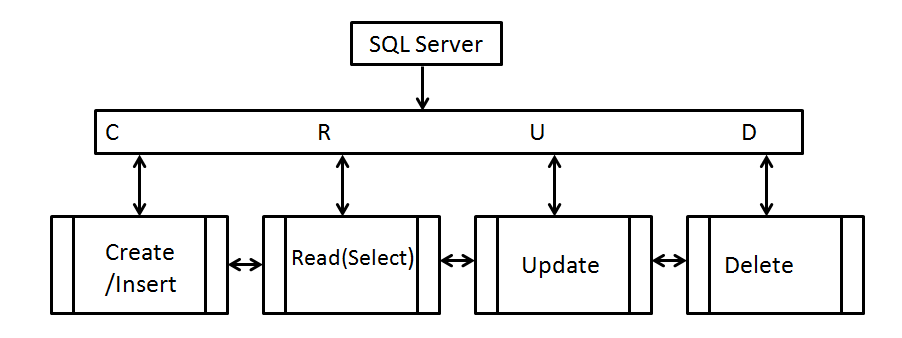
CRUD
CRUD is an acronym that stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete. These are the four most basic operations that can be performed with most traditional database systems and they are the backbone for interacting with any database.CRUD is an acronym that stands for CREATE, READ, UPDATE, and DELETE. In SQL Server, CRUD is represented by 4 operations performed on the selected data against a specific SQL database: CREATE refers to inserting columns and values into the table.
Status codes.
Status codes are issued by a server in response to a client’s request made to the server. It includes codes from IETF Request for Comments (RFCs), other specifications, and some additional codes used in some common applications of the HTTP.
- 100’s :
The HTTP 100 Continue informational status response code indicates that everything so far is OK and that the client should continue with the request or ignore it if it is already finished.
- 200’s :
The HTTP 200 OK success status response code indicates that the request has succeeded. A 200 response is cacheable by default. The meaning of a success depends on the HTTP request method: GET : The resource has been fetched and is transmitted in the message body.
- 300’s :
The HTTP 300 Multiple Choices redirect status response code indicates that the request has more than one possible responses. The user-agent or the user should choose one of them. As there is no standardized way of choosing one of the responses, this response code is very rarely used.
- 400’s :
The HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 400 Bad Request response status code indicates that the server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
- 500’s:
The HTTP status code 500 is a generic error response. It means that the server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. This error is usually returned by the server when no other error code is suitable.

status code 202
The 202 response is intentionally non-committal. Its purpose is to allow a server to accept a request for some other process (perhaps a batch-oriented process that is only run once per day) without requiring that the user agent’s connection to the server persist until the process is completed.
status code 308
The HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 308 Permanent Redirect redirect status response code indicates that the resource requested has been definitively moved to the URL given by the Location headers. … Note: Some Web applications may use the 308 Permanent Redirect in a non-standard way and for other purposes.
.
update didn’t return data
{‘code’: ‘UPGRADE_NEEDED’, ‘message’: ‘Please upgrade to version 2.0.’}
Forbidden :
The HTTP 403 Forbidden client error status response code indicates that the server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. … The access is permanently forbidden and tied to the application logic, such as insufficient rights to a resource. What is a 403 Forbidden Error? …
- Refresh the Page.
- Double Check the Address.
- Clear Your Browser Cookies and Cache.
- Check if You Have Permission to Access the URL.
- Try Again Later.
- Contact the Website.
- Contact your ISP.
MongoDB
You should see a file named mongo , which is the shell executable. If you do not have mongo shell installed, follow the install directions for your environment.To connect to your local MongoDB, you set Hostname to localhost and Port to 27017 . These values are the default for all local MongoDB connections (unless you changed them). Press connect, and you should see the databases in your local MongoDB.
middleware
Middleware is software that provides common services and capabilities to applications outside of what’s offered by the operating system. Data management Middleware is software which lies between an operating system and the applications running on it. Common middleware examples include database middleware, application server middleware, message-oriented middleware, web middleware and transaction-processing monitors.
What does app.use(express.json()) do ?
express. json() is a method inbuilt in express to recognize the incoming Request Object as a JSON Object. This method is called as a middleware in your application using the code: app.

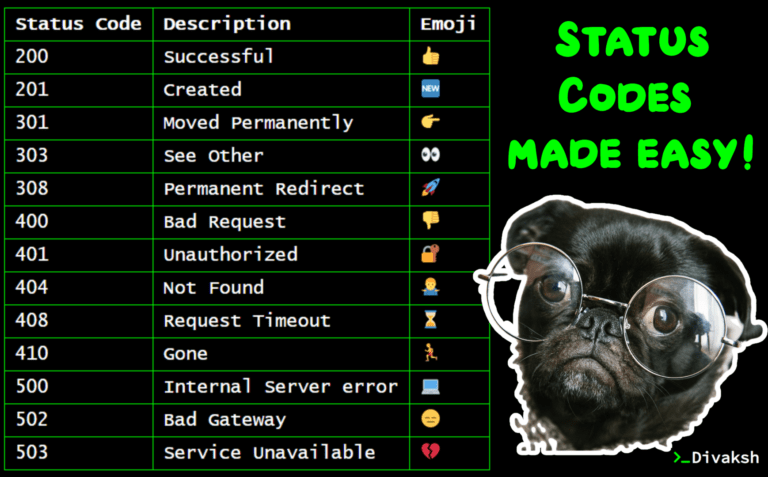
Things I want to know more about.
solveing this error
for more info please visit my github
## qusaiqeisi
best regard