Authentication
What is OAuth?
OAuth allows websites and services to share assets among users. It is widely accepted, but be aware of its vulnerabilities.

OAuth definition
OAuth is an open-standard authorization protocol or framework that describes how unrelated servers and services can safely allow authenticated access to their assets without actually sharing the initial, related, single logon credential. In authentication parlance, this is known as secure, third-party, user-agent, delegated authorization.
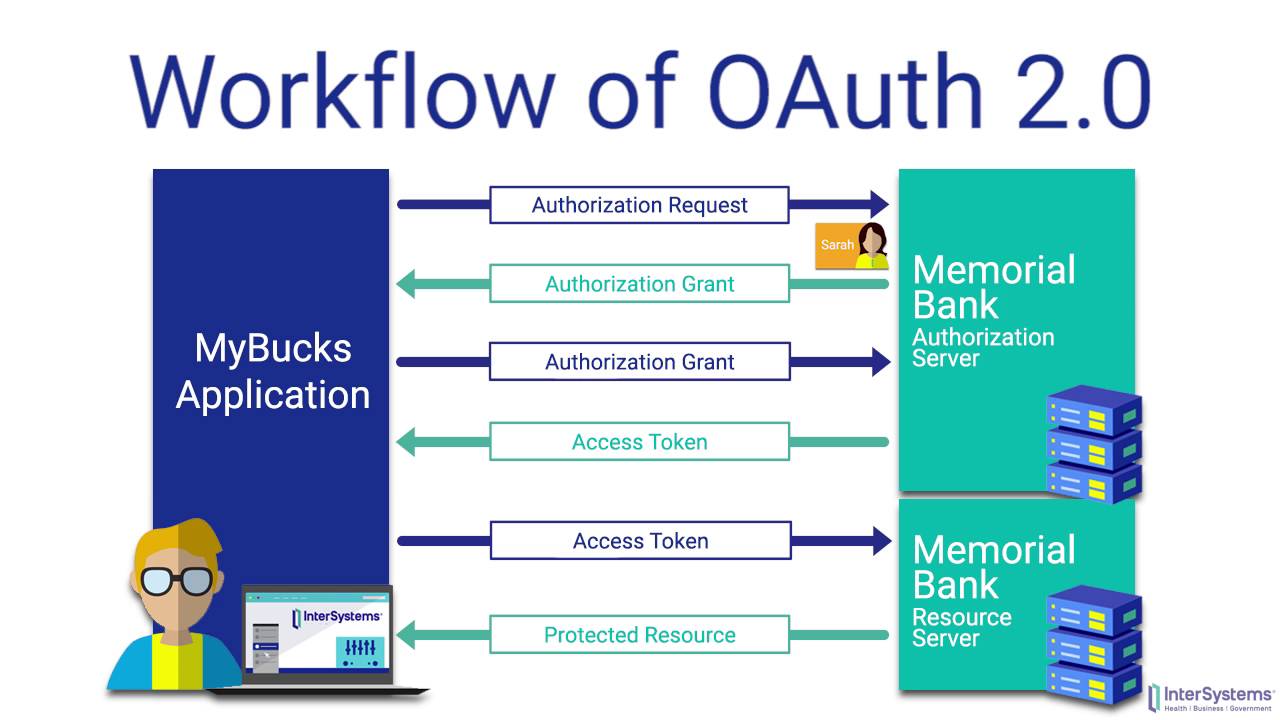
How OAuth works
Let’s assume a user has already signed into one website or service (OAuth only works using HTTPS). The user then initiates a feature/transaction that needs to access another unrelated site or service.

- The first website connects to the second website on behalf of the user, using OAuth, providing the user’s verified identity.
- The second site generates a one-time token and a one-time secret unique to the transaction and parties involved.
- The first site gives this token and secret to the initiating user’s client software.
- The client’s software presents the request token and secret to their authorization provider (which may or may not be the second site).
- If not already authenticated to the authorization provider, the client may be asked to authenticate. After authentication, the client is asked to approve the authorization transaction to the second website.
- The user approves (or their software silently approves) a particular transaction type at the first website.
- The user is given an approved access token (notice it’s no longer a request token).
- The user gives the approved access token to the first website. The first website gives the access token to the second website as proof of authentication on behalf of the user.
- The second website lets the first website access their site on behalf of the user. The user sees a successfully completed transaction occurring.
- OAuth is not the first authentication/authorization system to work this way on behalf of the end-user.
Authentication and Authorization Flows
Auth0 uses the OpenID Connect (OIDC) Protocol and OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework to authenticate users and get their authorization to access protected resources. With Auth0, you can easily support different flows in your own applications and APIs without worrying about OIDC/OAuth 2.0 specifications or other technical aspects of authentication and authorization.
Hybrid Flow
Applications that are able to securely store Client Secrets may benefit from the use of the Hybrid Flow, which combines features of the Authorization Code Flow and Implicit Flow with Form Post to allow your application to have immediate access to an ID token while still providing for secure and safe retrieval of access and refresh tokens. This can be useful in situations where your application needs to immediately access information about the user, but must perform some processing before gaining access to protected resources for an extended period of time. The Hybrid Flow is an OpenID Connect flow which incorporates characteristics of both the Implicit flow and the Authorization Code flow. It enables clients to obtain some tokens straight from the Authorization Endpoint, while still having the possibility to get others from the Token Endpoint.

Things I want to know more about
solveing this error.
for more info please visit my github
## qusaiqeisi
best regard