Chart.j
Chart. js is a community maintained open-source library (it’s available on GitHub) that helps you easily visualize data using JavaScript. It’s similar to Chartist and Google Charts. It supports 8 different chart types (including bars, lines, & pies), and they’re all responsive.Charts are far better for displaying data visually than tables and have the added benefit that no one is ever going to press-gang them into use as a layout tool. They’re easier to look at and convey data quickly, but they’re not always easy to create.
Chart Types
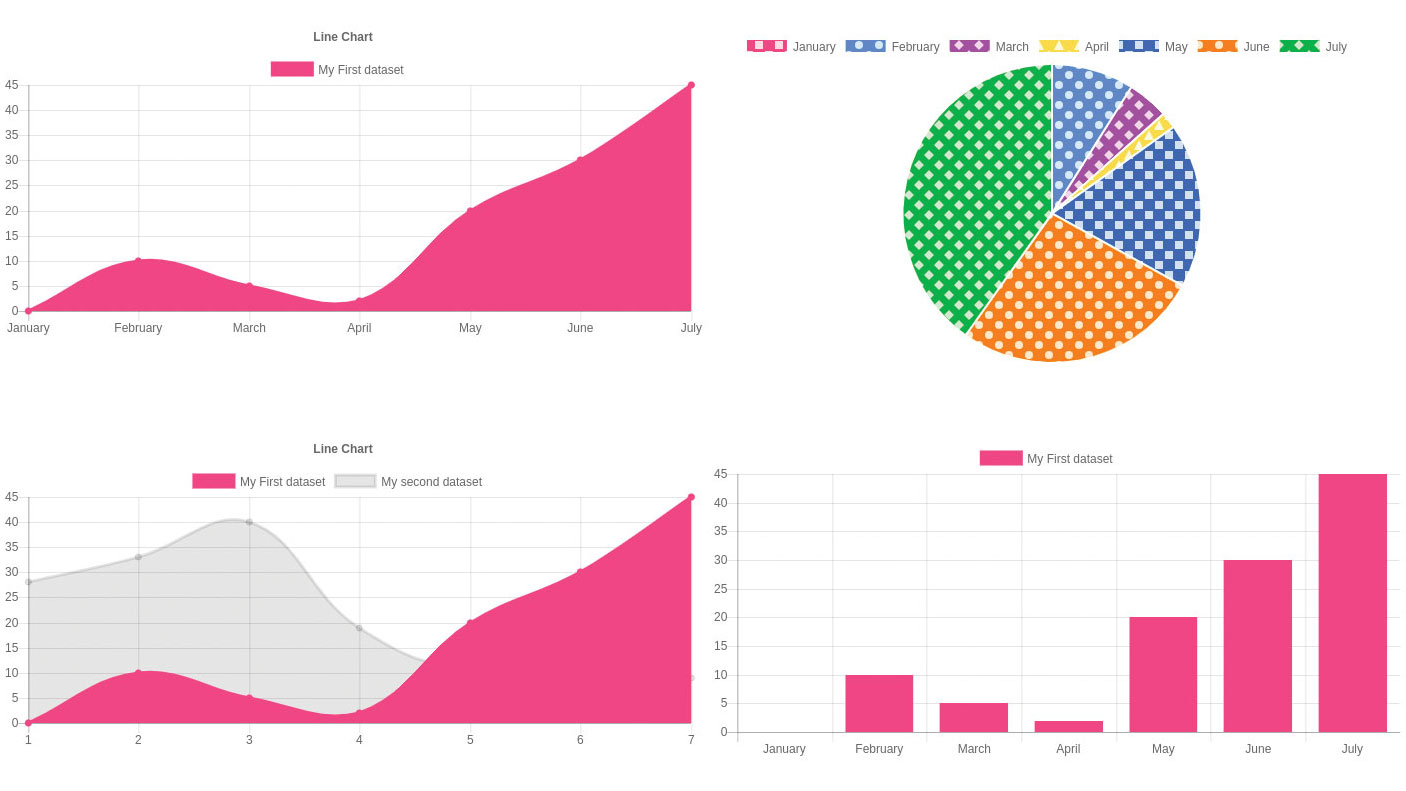
- Bar Chart. Bar charts are one of the most common * * data visualizations. …
- Line Chart. The line chart, or line graph, connects several distinct data points, presenting them as one continuous evolution. …
- Pie Chart. …
- Maps. …
- Density Maps. …
- Scatter Plot. …
- Gantt Chart. …
- Bubble Chart.
![]()
canvas
canvas> is an HTML element which can be used to draw graphics via scripting (usually JavaScript). This can, for instance, be used to draw graphs, combine photos, or create simple (and not so simple) animations. … This tutorial describes how to use the canvas> element to draw 2D graphics, starting with the basics.
- Basic usage.
- Drawing shapes.
- Applying styles and colors.
- Drawing text.
- Using images.
- Transformations.
- Compositing and clipping.
- Basic animations.

Providing fallback content is very straightforward: just insert the alternate content inside the canvas> element. Browsers that don’t support canvas> will ignore the container and render the fallback content inside it. Browsers that do support canvas> will ignore the content inside the container, and just render the canvas normally.
Drawing shapes with canvas
Before we can start drawing, we need to talk about the canvas grid or coordinate space. Our HTML skeleton from the previous page had a canvas element 150 pixels wide and 150 pixels high. To the right, you see this canvas with the default grid overlayed. Normally 1 unit in the grid corresponds to 1 pixel on the canvas. The origin of this grid is positioned in the top left corner at coordinate (0,0). All elements are placed relative to this origin. So the position of the top left corner of the blue square becomes x pixels from the left and y pixels from the top, at coordinate (x,y). Later in this tutorial we’ll see how we can translate the origin to a different position, rotate the grid and even scale it, but for now we’ll stick to the default.
Applying styles and colors
n the chapter about drawing shapes, we used only the default line and fill styles. Here we will explore the canvas options we have at our disposal to make our drawings a little more attractive. You will learn how to add different colors, line styles, gradients, patterns and shadows to your drawings.
Colors
Up until now we have only seen methods of the drawing context. If we want to apply colors to a shape, there are two important properties we can use: fillStyle and strokeStyle.
fillStyle = color Sets the style used when filling shapes. strokeStyle = color Sets the style for shapes’ outlines. color is a string representing a CSS color>, a gradient object, or a pattern object. We’ll look at gradient and pattern objects later. By default, the stroke and fill color are set to black (CSS color value #000000).
Drawing text
The canvas rendering context provides two methods to render text: fillText(text, x, y [, maxWidth]) Fills a given text at the given (x,y) position. Optionally with a maximum width to draw. strokeText(text, x, y [, maxWidth]) Strokes a given text at the given (x,y) position. Optionally with a maximum width to draw.

short quiz
- what is color?
- what is chart ?
- what is drowing text ?
for more info please visit my github qusaiqeisi
best regard