HTML Lists
HTML lists allow web developers to group a set of related items in lists.
Unordered HTML List
UL Element - The full name of the UL Element is the Unorder List. Unorder List Element is created by Bullet Lists or Unorder Lists.
Ordered List
Order List is also called Numbered List. OL is used to show one type of information in unit fixed order. The OL List is written before the Number Order in the list item.
Definition Lists
Definition List is the most appropriate element to tell the meaning of a particular dictionary, Online Dictionaries, Glossary Definition. Because this List type is defined in the first Definition Term. Then the meaning of that term is enumerated. The texture of this list is like the dictionary.
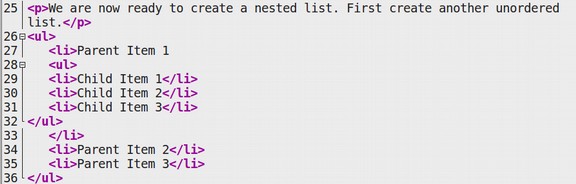
Nested Lists
Nested List is not a type of HTML type. But, we’ve included it here as a 4th type. This is just like the purpose of simplifying the List Concept. So that the learners have the facility to learn.

HTML Boxes
In CSS, the term “box model” is used when talking about design and layout. The CSS box model is essentially a box that wraps around every HTML element. It consists of: margins, borders, padding, and the actual content

Box Dimensions
width, height its to control the size of the text by have which called max width and max hight .min width and min hight
Overflowing Content
The overflow property specifies whether to clip the content or to add scrollbars when the content of an element is too big to fit in the specified area.
- hidden This property simply hides any extra content that does not fit in the box.
- scroll This property adds a scrollbar to the box so that users can scroll to see the missing content
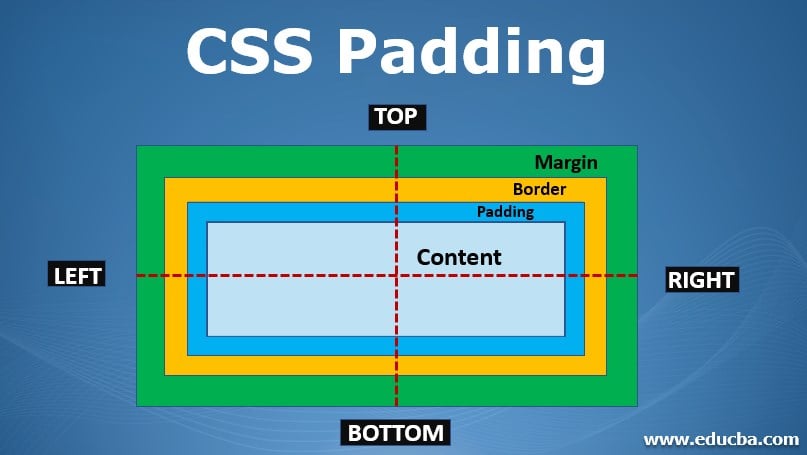
Border, Margin & Padding
- Border
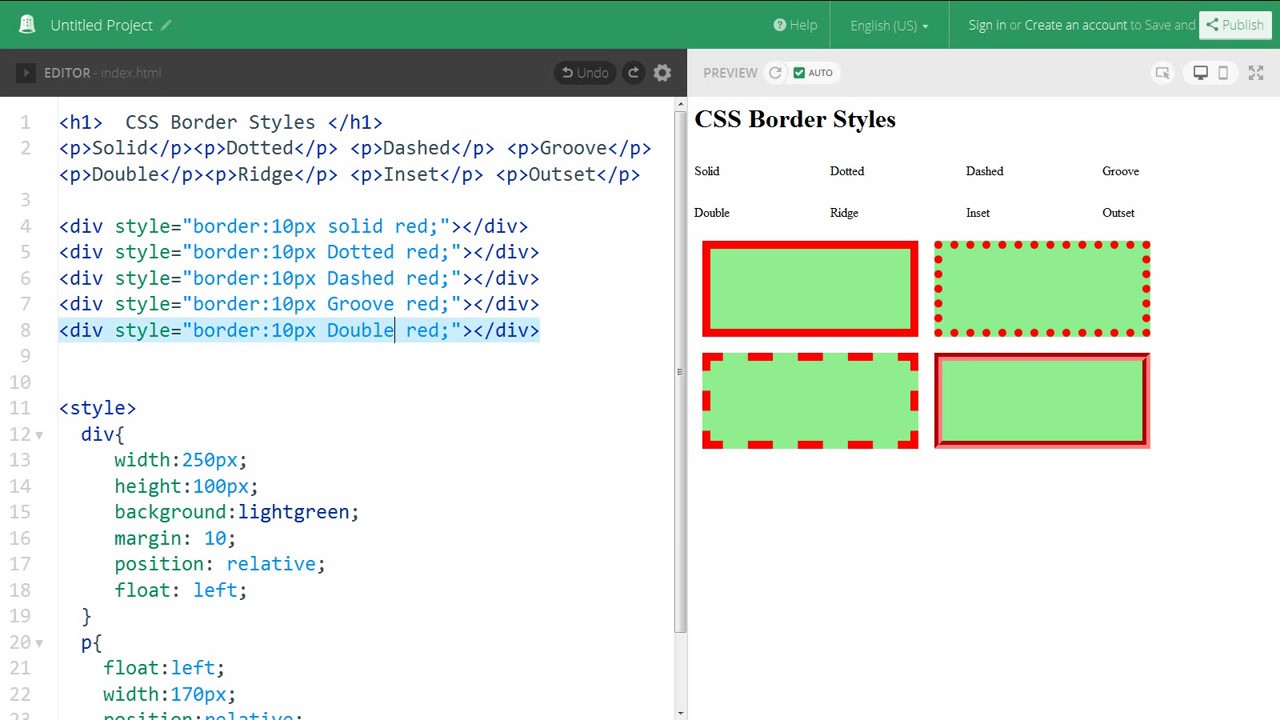
The CSS border properties allow you to specify the style, width, and color of an element’s border.
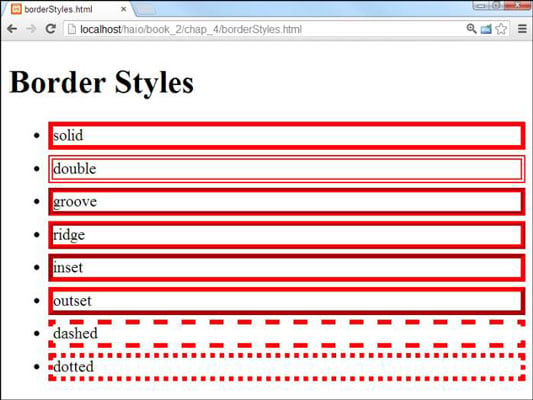
The border-style property specifies what kind of border to display.
The following values are allowed:
- dotted - Defines a dotted border
- dashed - Defines a dashed border
- solid - Defines a solid border
- double - Defines a double border
- groove - Defines a 3D grooved border. The effect depends on the border-color value
- ridge - Defines a 3D ridged border. The effect depends on the border-color value
- inset - Defines a 3D inset border. The effect depends on the border-color value
- outset - Defines a 3D outset border. The effect depends on the border-color value
- none - Defines no border
- hidden - Defines a hidden border
- The border-style property can have from one to four values (for the top border, right border, bottom border, and the left border).
- padding
Padding is used to create space around an element’s content, inside of any defined borders.
- Padding - Individual Sides CSS has properties for specifying the padding for each side of an element: padding-top padding-right padding-bottom padding-left All the padding properties can have the following values: length - specifies a padding in px, pt, cm, etc. % - specifies a padding in % of the width of the containing element inherit - specifies that the padding should be inherited from the parent element
- Padding - Shorthand Property
The padding property is a shorthand property for the following individual padding properties: padding-top padding-right padding-bottom padding-left So, here is how it works: If the padding property has four values: padding: 25px 50px 75px 100px; top padding is 25px right padding is 50px bottom padding is 75px left padding is 100px
CSS3
- Border Images
The border-image property applies an image to the border of any box. It takes a background image and slices it into nine pieces.
- Box Shadows
The box-shadow property allows you to add a drop shadow around a box. It works just like the text-shadow property that you met on page 288. It must use at least the first of these two values as well as a color.

Basic JavaScript Instructions
JavaScript (“JS” for short) is a full-fledged dynamic programming language that can add interactivity to a website. JavaScript itself is relatively compact, yet very flexible. Developers have written a variety of tools on top of the core JavaScript language, unlocking a vast amount of functionality with minimum effort.A script is made up of a series of statements. Each statement is like a step in a recipe. Scripts contain very precise instructions. For example, you might specify that a value must be remembered before creating a calculation using that value. Variables are used to temporarily store pieces of information used in the script. Arrays are special types of variables that store more than one piece of related information. JavaScript distinguishes between numbers (0-9), strings (text), and Boolean values (true or false). Expressions evaluate into a single value. Expressions rely on operators to calculate a value.
SWITCH STATEMENTS
The switch statement evaluates an expression. The value of the expression is then compared with the values of each case in the structure. If there is a match, the associated block of code is executed. The switch statement is often used together with a break or a default keyword (or both).
he purpose of the switch statement is to present the user with a different message depending on which level they are at. The message is stored in a variable called msg
TYPE COERCION & WEAK TYPING
JavaScript can convert data types behind the scenes to complete an operation. This is known as type coercion. For example, a string ‘l ‘ could be converted to a number 1 in the following expression:(‘ 1’ > 0). As a result, the above expression would evaluate to true. JavaScript is said to use weak typing because the data type for a value can change. Some other languages require that you specify what data type each variable will be. They are said to use strong typing.
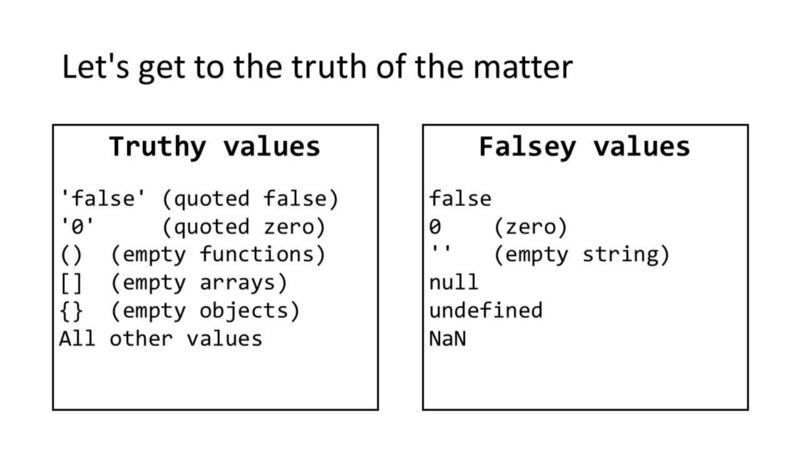
TRUTHY & FALSY VALUES Truthy values are treated as if they are true. Almost everything that is not in the falsy table can be treated as if it were true. Falsy values are treated as if they are fa 1 se. The table to the left shows a hi ghScore variable with a series of values, all of which are falsy.
loop
for and while
loop counter
 its ti give the user the chouse to have many number that he need it
its ti give the user the chouse to have many number that he need it
short quiz :
- what is loop ?
- how border works ?
- what is CSS ?
- define part of HTML ?
- short note about java instruction ?
for more info please visit my github qusaiqeisi
best regard