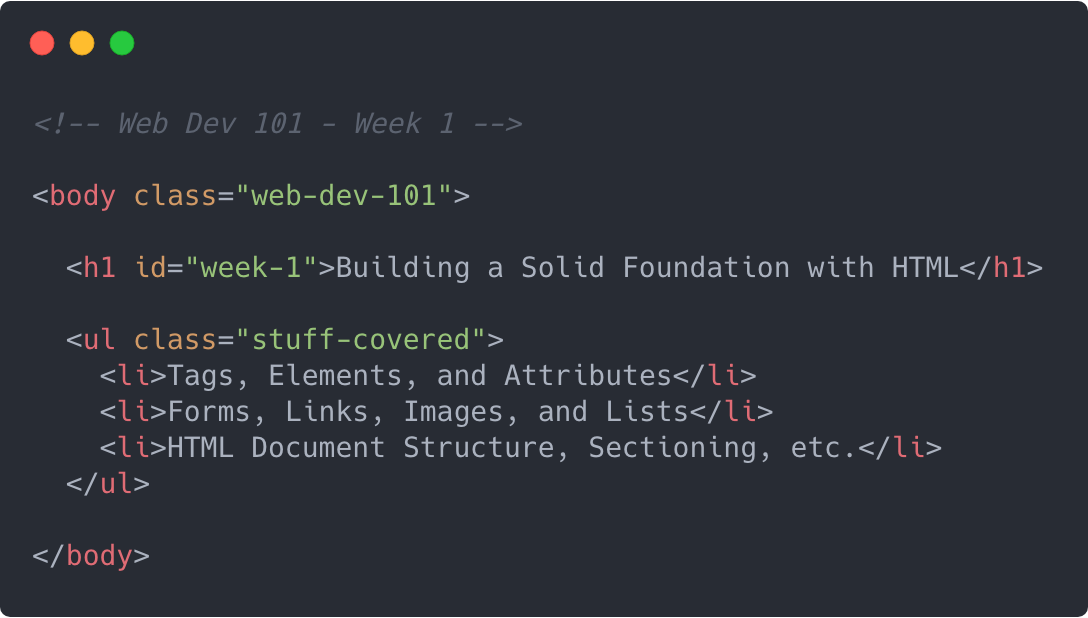
HTML
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
the HTML is the way that we creat page structer and design fpr the clint .
**its content 2 mager part **
head
the titel of the page in url you can see it
body
what you writ what you read and the user can read it also
we use some elemant to have the structer.
The Nav Element. …
The Section and Article Elements. …
The Aside Element. …
Taking Care of Internet Explorer. …
Conclusion.
DOCTYPES tell browsers which version of HTML you
are using.
X You can add comments to your code between the
markers.
X The id and class attributes allow you to identify
particular elements.
X cut windows into your web pages through
which other pages can be displayed.
X Escape characters are used to include special
characters in your pages such as <, >, and ©.
X The <div> and elements allow you to group
block-level and inline elements together.
X The
example
HTML5 Layout
Headers & Footers
> where we writ the main titel and the referance of te page like the claoseing and copy right .
* The main header or footer
that appears at the top or
bottom of every page on the
site.
* A header or footer for an
individual or
within the page.
The sectioning elements in HTML5 are , , , and . is also kind of a sectioning element since all content lying inside of it is part of the default document section.
Here is a brief explanation of each sectioning element and how they are used:
* – Equivalent to role="navigation". Major site navigation that consistently appears frequently across the site. Examples include the primary navigation, secondary navigation, and in-page navigation.
* – Equivalent to role="complementary". Content that is only tangentially related (or not related) to the main content. Think of something like a sidebar with supplementary information, a note within an article, or the outer container for a list of related articles at the bottom of a blog post.
* – Equivalent to role="article". Content that is self-contained in that it makes sense on its own when taken out of context. That could mean a widget, a blog post or even a comment within a blog post.
* – Equivalent to role="region". Content that needs extra context from its parent sectioning element to make sense. This is a generic sectioning element that is used whenever it doesn’t make sense to use the other more semantic ones

## Process & Design
> when we design page we have to make the study about the user age.background . education and intrest then we can have the page that can fit the use
**sitmap**

> allow you to understand te page and its purpuse .The aim is to create a diagram
of the pages that will be used
to structure the site. This is
known as a site map and it will
show how those pages can be
grouped.
To help you decide what
information should go on each
page, you can use a technique
called card sorting.
**WireFrames**

> A lot of designers will take the
elements that need to appear on
each page and start by creating
wireframes. This involves
sketching or shading areas
where each element of the page
will go (such as the logo, primary
navigation, headings and main
bodies of text, user logins etc).
By creating a wireframe you can
ensure that all of the information
that needs to be on a page is
included.
**short note **
| tag | Element content | End tag |
| :--- | :---: | ---: |
| | My First Heading | |
| | My First paragraph |
|
| | link | |
## The ABC of Programming
> A B C
#### waht is A?
>A script is a series of instructions that the computer
can follow in order to achieve a goal.
Each time the script runs, it might only use a subset of
all the instructions.
Computers approach tasks in a different way than
humans, so your instructions must let the computer
solve the task prggrammatically.
To approach writing a script, break down your goal into
a series of tasks and then work out each step needed
to complete that task (a flowchart can help).
#### waht is B?
> computer use code to fit the opject and the event .so it use html for the structercode and applie it to see it as phiscal opject.
and use the cade to make it interactive wit the user to sow him as example "welcome to my page"
#### how do i use C?
> It is best to keep JavaScript code in its own JavaScript
file. JavaScript files are text files (like HTML pages and
CSS style sheets), but they have the . j s extension.
The HTML
 and the elemant use tag that make you give the style that we use it fir the page
and the elemant use tag that make you give the style that we use it fir the page
 An Introduction to the HTML5 Structural Elements
Create an HTML5 Page. Let’s explore the new elements by building a sample page. …
The Header Element. HTML5 semantics come into play with all of the new elements. …
*The Footer Element. …
An Introduction to the HTML5 Structural Elements
Create an HTML5 Page. Let’s explore the new elements by building a sample page. …
The Header Element. HTML5 semantics come into play with all of the new elements. …
*The Footer Element. … HTML pages are text documents.
X HTML uses tags (characters that sit inside angled
brackets) to give the information they surround special
meaning.
X Tags are often referred to as elements.
X Tags usually come in pairs. The opening tag denotes
the start of a piece of content; the closing tag denotes
the end.
X Opening tags can carry attributes, which tell us more
about the content of that element.
X Attributes require a name and a value.
X To learn HTML you need to know what tags are
available for you to use, what they do, and where they
can go
HTML pages are text documents.
X HTML uses tags (characters that sit inside angled
brackets) to give the information they surround special
meaning.
X Tags are often referred to as elements.
X Tags usually come in pairs. The opening tag denotes
the start of a piece of content; the closing tag denotes
the end.
X Opening tags can carry attributes, which tell us more
about the content of that element.
X Attributes require a name and a value.
X To learn HTML you need to know what tags are
available for you to use, what they do, and where they
can go