Linked Lists
Linked Lists
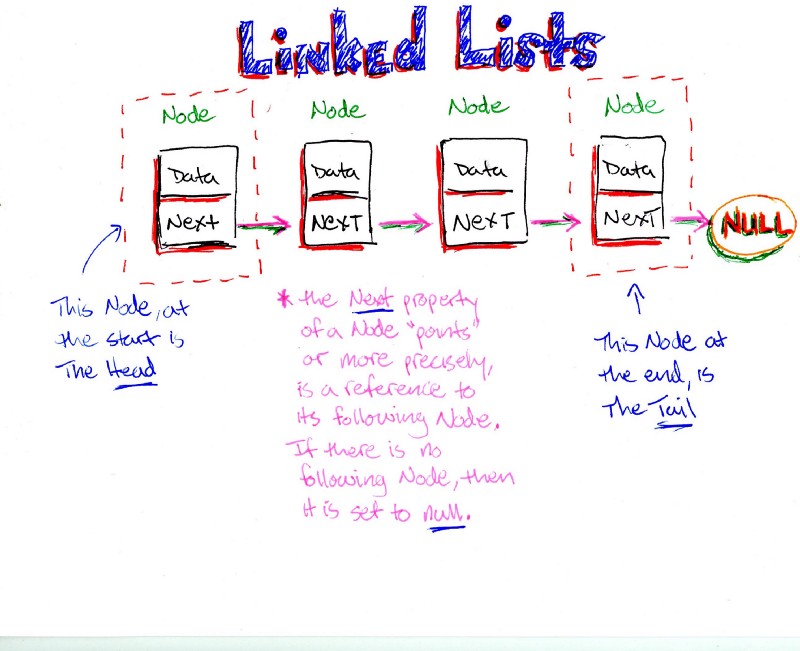
- linked list is a collection of nodes, starting with head object that will be null when the linked list is empty, then when adding the first node will update the value of the head to this node object, including the next propert that will point to the reference of the next node if it exist or null if it was the last node in the linked list.
Terminology
- linked list contain nodes that point to the next node .
- singly mean its point to one reference which is the next node .
- doubly mean its point to two next references and previous .
- node its the item\links(data) that live in the node .
- next its property exist in the node .
- head its reference to the first node .
- Current its the node that we looking into it .
- if we add a node to the first BigO of time will be O(1), but if we add between nodes or at the end, BigO of time will be O(n). and in the both cases the BigO of space will be as the value of nodes, and mostly will be O(1).
- there are two types of linked lists : singly & doubly; the difference is the singly only have one pointer to the next node. but the doubly has two pointers; the first one for the next node and the second one for the previous node.
data structures
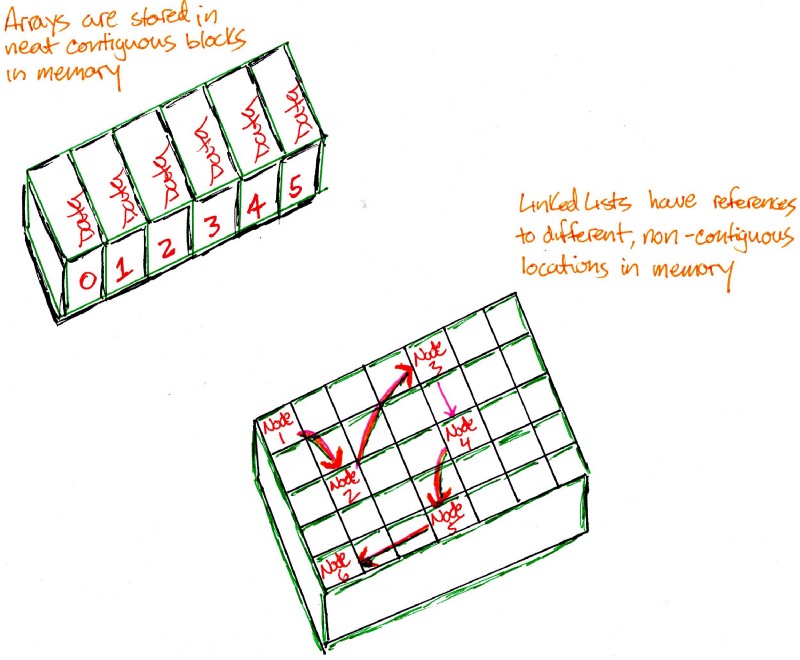
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes which together represent a sequence.
Linked List is a very commonly used linear data structure which consists of group of nodes in a sequence. Each node holds its own data and the address of the next node hence forming a chain like structure. Linked Lists are used to create trees and graphs
Time Complexity
- Insertion
- insertHead, appendToTail — O(1)
- if a specific node is known, insertAfter — O(1)
Deletion
- removeHead — O(1);
- if a specific node is known, removeAfter — O(1)
- if the node is not known — O(N)
- Traversing
- findNode, forEach, print — O(N)
Linked List?
- O(1) : means i need a constant time & and same space, and doesn’t matter how much the elements we have or how huge our input is.
- O(n) : means that as our input grows, the space and time that we need to run that algorithm grows linearly.
- a linked list is usually efficient when it comes to adding and removing most elements, but can be very slow to search and find a single element. data structures : ways of organizing our data.
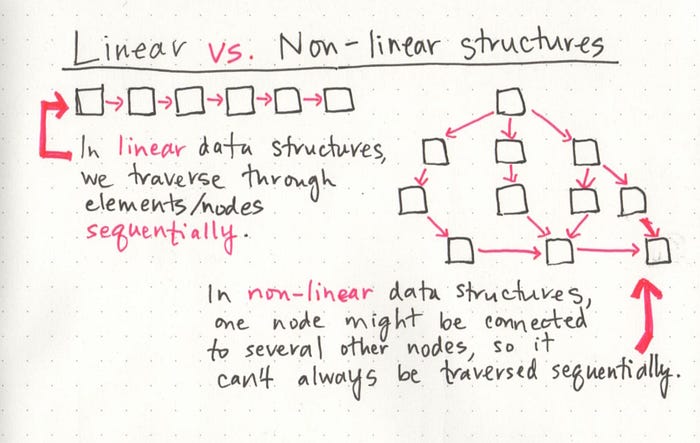
- linked lists are a linear data structure, that means we traversed over the data sequentially.
- arrays and linked lists are linear data structure.
so the thing is what you abeal to do and achive to undersatnd your coworker team
source
……………… linked list ……………… What’s a Linked List, Anyway pt1 ……………… What’s a Linked List, Anyway pt1
for more info please visit my github qusaiqeisi
best regard