Graphs :
Graph :
- A graph is a non-linear data structure that can be looked at as a collection of vertices (or nodes) potentially connected by line segments named edges.

Vertex :
- or node means the data object that can has other adjacent vertices or not.a vertex (plural vertices) or node is the fundamental unit of which graphs are formed.
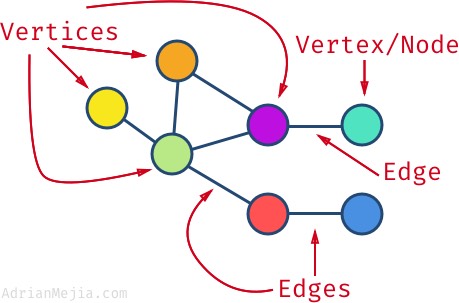
Edge :
- the connection between two nodes.
Degree :
- number of edges that the node has.
Neighber :
- the connected nodes to the node.
Directed & unDirected Graph
-
Directed or called Digraph : that the edge has a direction and one of two connected nodes has the other, and the other one hasn’t. (uni-directional)
-
unDirected : both of them has the other node. (bi-directional)

complete graph :
- when each node connected to all other nodes.
connected :
- when no node doesn’t has least one edge or doesn’t connected at least to one node.
Dusconnected graph :
- when one or more nodes doesn’t has any edge or node.
directed acyclic graph is also called a DAG :
- when no cycle happen in the graph.
Cyclic Graphs :
- when starts with node and returns to the same node.
Weighted Graphs :
- A weighted graph is a graph with numbers assigned to its edges. These numbers are called weights.
We represent graphs through:
- Adjacency Matrix : by two dimensional array.
- Adjacency List : it is a collection of linked lists or array that lists all of the other vertices that are connected.
- in weighted graphs you must include both the weight and the name of the adjacent vertex.
Traversals :
-
will do traversals in graph with breadth first and depth first methods.
Real applications of graphs :
1. GPS and Mapping
2. Driving Directions
3. Social Networks
4. Airline Traffic
5. Netflix uses graphs for suggestions of products
so the thing is what you abeal to do and achive to undersatnd your coworker team
for more info please visit my github
best regard