Context API - Behaviors .
When you have multiple contexts, what component type should you use (class/function) and why?
.Context is designed to share data that can be considered “global” for a tree of React components, such as the current authenticated user, theme, or preferred language.In class components, the render method will be called, whenever the state of the components changes. On the other hand, the Functional components render the UI based on the props. Class Components should be preferred whenever we have the requirement with the state of the component.
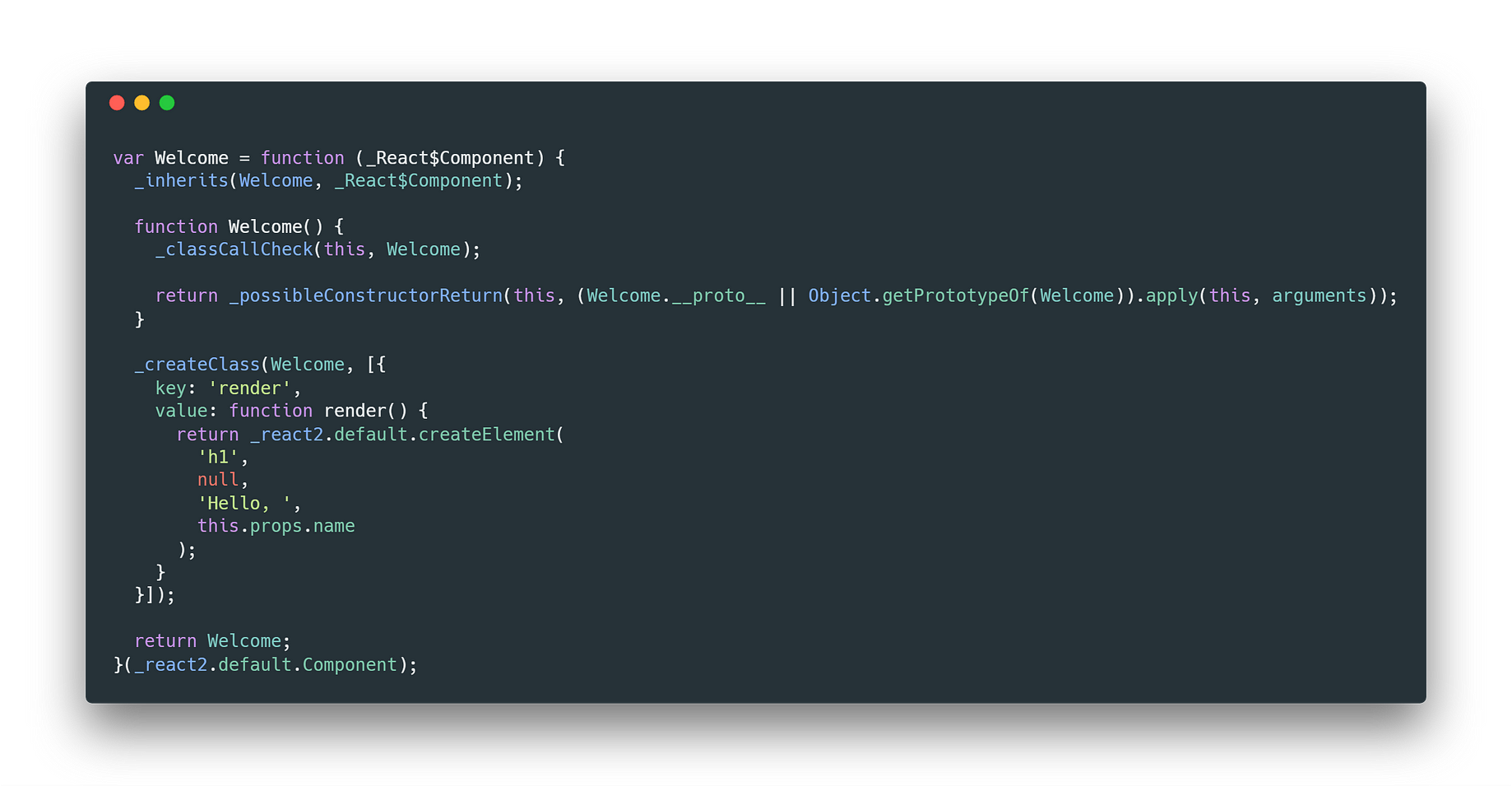
What are some good use cases for using the Context API for global state?
From React’s own docs they say that Context provides a way to pass data through the component tree without having to pass props down manually at every level. Great! That sounds exactly like what we are looking for. In combination with the useContext and useReducer hooks we can create a global store that manages the entire app’s state and supports convenient ways to update the state throughout the app regardless of how deep the component tree goes.

How can you best test context?
React Context is a tool for designing flexible Component APIs. How we test it depends on the situation, we are going to explore some of the situations you might find yourself in and the best way to write maintainable tests for each of them.The best way to test Context is to make our tests unaware of its existence and avoiding mocks. We want to test our components in the same way that developers would use them (behavioral testing) and mimic the way they would run in our applications (integration testing).
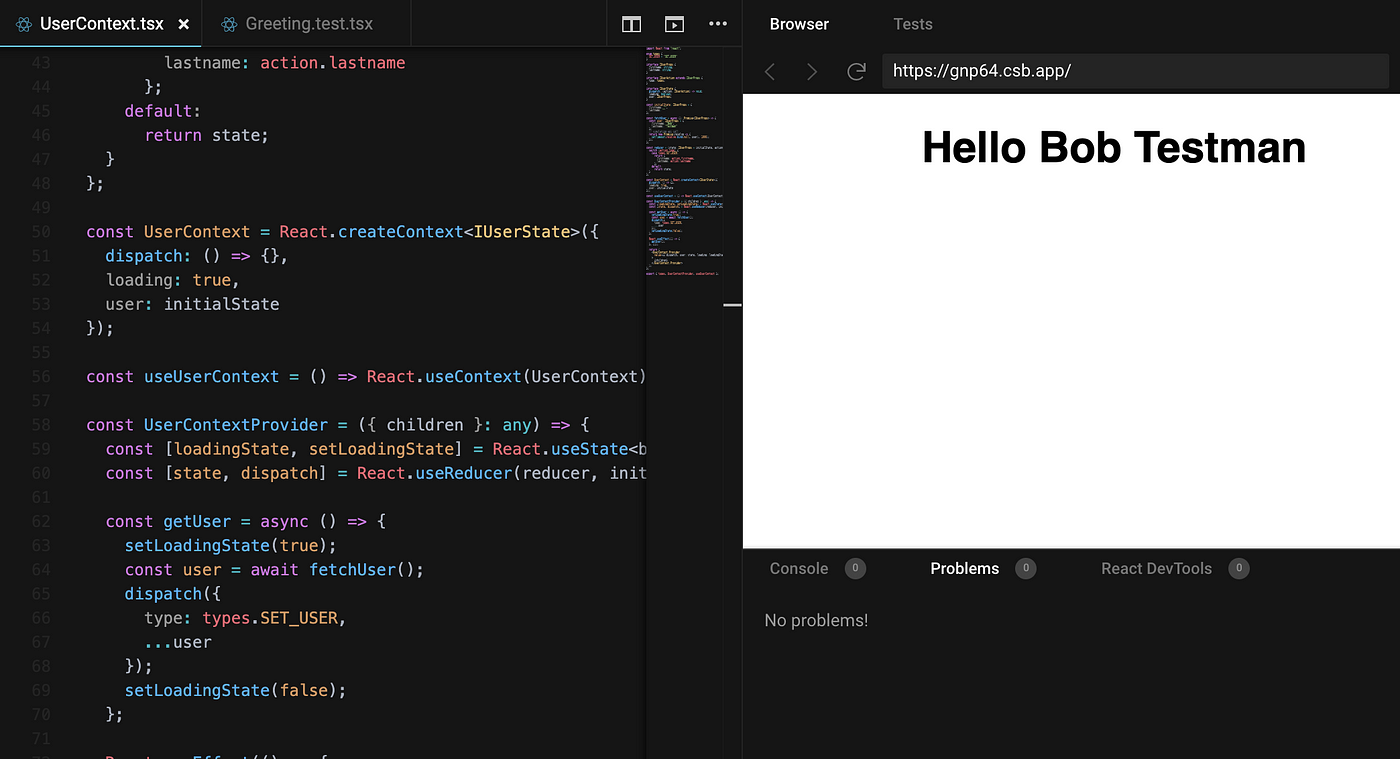
Document the following Vocabulary Terms
- context :
Context is the background, environment, setting, framework, or surroundings of events or occurrences. Simply, context means circumstances forming a background of an event, idea or statement, in such a way as to enable readers to understand the narrative or a literary piece.
- useContext()
used to create common data that can be accessed throughout the component hierarchy without passing the props down manually to each level. Context defined will be available to all the child components without involving “props”.
- static context :
A static method or, block belongs to the class and these will be loaded into the memory along with the class. You can invoke static methods without creating an object. … But static contexts(methods and blocks) doesn’t have any instance they belong to the class
so the thing is what you abeal to do and achive to undersatnd your coworker team
for more info please visit my github
best regard